- Overview
- Causes, Risks & Prevention
- Symptoms & Types
- Tests & Diagnosis
- Your Cancer Care Team
- Treatment & Side Effects
- Treatment Support
- Living With
- Remission & Recurrence
- Support & Resources
- Appointment Prep
- View Full Guide
Understanding Renal Cell Carcinoma

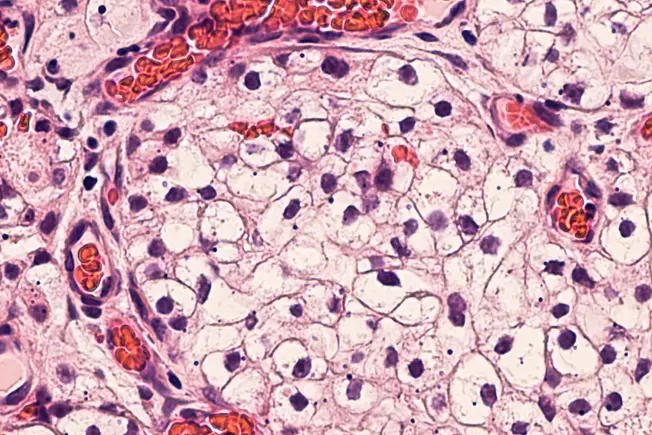
What Is Renal Cell Carcinoma?
It's the most common type of kidney cancer. Most people who have renal cell carcinoma are older, usually between the ages of 50 and 70. It often starts as just one tumor in a kidney but sometimes begins as several tumors.

Causes
Scientists aren't sure exactly what causes renal cell carcinoma. Some things can raise your chances of getting the disease, such as smoking, being very overweight, and exposure to certain dyes, asbestos, cadmium, herbicides, and solvents.

Symptoms
Early on, renal cell carcinoma doesn't usually cause symptoms. As the disease gets more serious, you might have warning signs like blood in your pee, persistent back pain, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.

Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose renal cell carcinoma using physical exams, urine and blood tests, biopsies, a type of X-ray called a CT scan, and ultrasound, which uses sound waves to take a picture of the organs inside your body
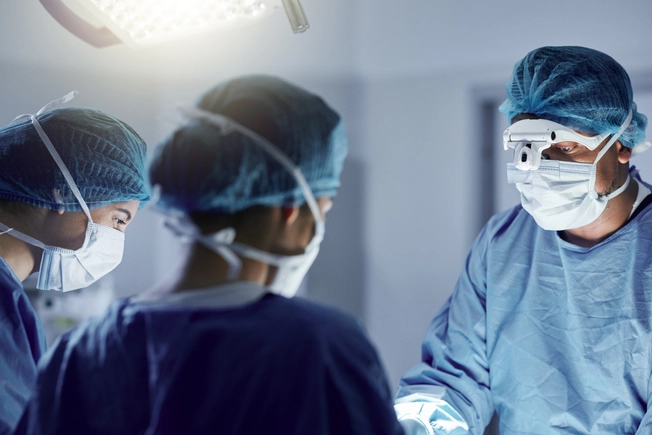

Surgery and Ablation
Your doctor may recommend surgery to remove part or all of your affected kidney. Another option is ablation. This uses extreme cold or radio waves to destroy tumors.
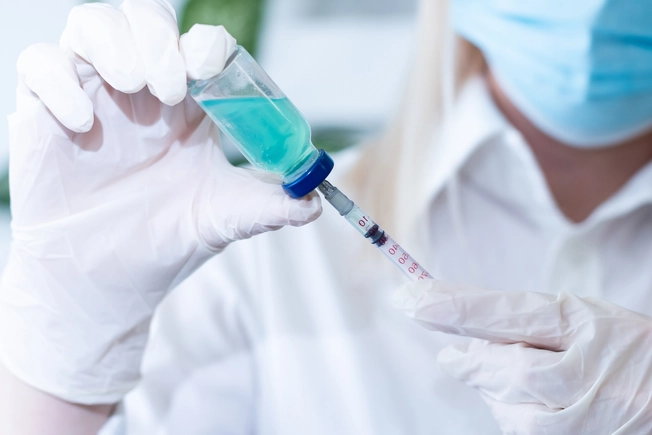
Biologics and Immunotherapy
Biologic and immunotherapy treatments boost your body's own defenses to fight cancer cells.
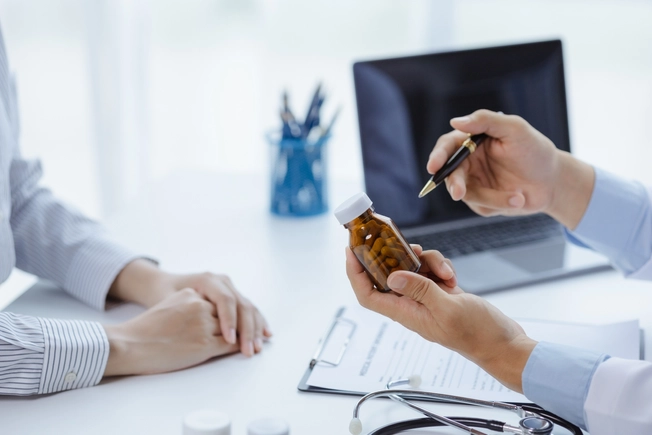

Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs designed to target specific molecules involved in tumor growth. These treatments attack specific things that cancers need to survive, such as a tumor's blood vessels or certain proteins.

Take Care of Yourself
You can do things during and after your treatment to feel stronger physically and emotionally. Eat smaller, more frequent meals to keep up your strength and nourish your body. Exercise is good for your mind and energy level. You may need to balance activity with periods of rest.
Photo Credits:
1) David A Litman/Shutterstock
2) Jelena Stanojkovic/Shutterstock
3) Ljupco Smokovski/Shutterstock
4) Natali _ Mis/Shutterstock
5) PeopleImages.com - Yuri A/Shutterstock
6) Andrew Angelov/Shutterstock
7) Pickadook/Shutterstock
8) SUPREEYA.CH/Shutterstock
SOURCES:
American Cancer Society: "Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma."
Medscape: "Renal Cell Carcinoma."
The Merck Manual: "Renal Cell Carcinoma."
National Cancer Institute: "General Information About Renal Cell Cancer;" "Renal Cell Cancer Treatment (PDQ®);" and "Renal Cell Cancer."